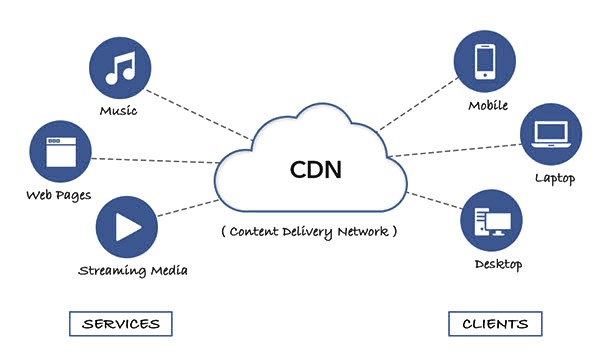
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a system of distributed servers strategically placed across different geographic locations to deliver content, such as web pages, videos, images, and other assets, to users more efficiently and quickly. The primary goal is to reduce latency, improve website performance, and enhance the user experience by bringing the content closer to the user’s location.
Table of Contents
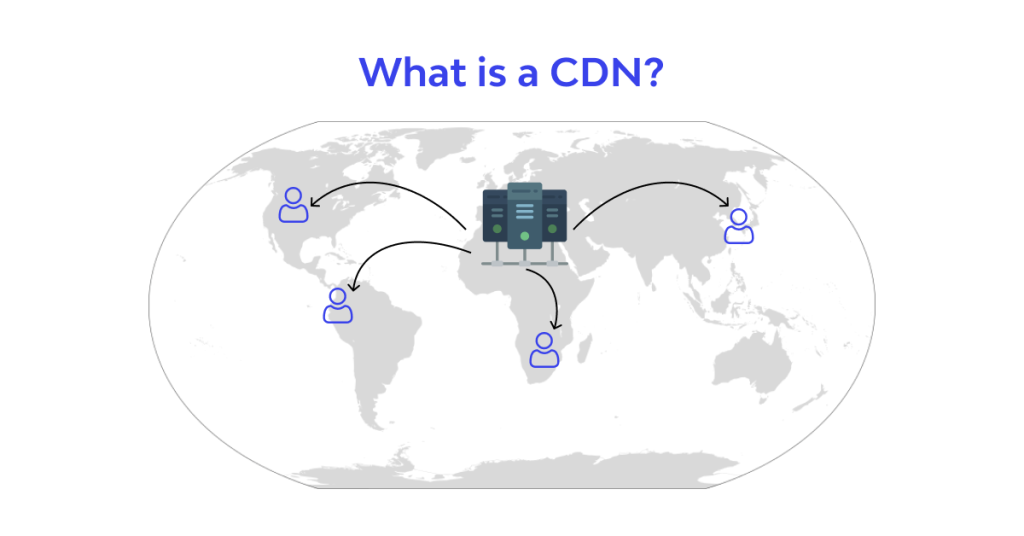
What is a content delivery network (CDN)?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of distributed servers designed to deliver web content and resources, such as images, videos, stylesheets, scripts, and more, to users in a faster, more reliable way. These servers are strategically placed in various geographic locations to ensure that content is delivered from a vps server that is physically closer to the user, reducing the time it takes for the data to travel.
Key Functions of a CDN:
- Content Distribution: CDNs distribute copies of content across multiple servers around the world. This allows users to download content from the server nearest to them, improving load times and reducing latency.
- Caching: Store cached versions of web content, such as static files (images, videos, etc.) on their servers. When a user requests content, serves it from the cached copy on the closest server instead of fetching it from the original (origin) server.
- Load Balancing: By distributing requests across various servers, can help balance traffic, preventing any single server from being overwhelmed during high traffic periods.
- Improving Speed: Since content is served from a closer server, reduce the distance data has to travel, speeding up delivery and improving the overall user experience.
- Enhancing Reliability: CDNs provide redundancy—if one server fails, another server in the network can serve the requested content, ensuring high availability and uptime.
- Security: Many CDNs offer features like DDoS protection, SSL/TLS encryption, and Web Application Firewalls (WAF), helping protect websites from cyber threats while delivering content efficiently.
How do CDNs work?
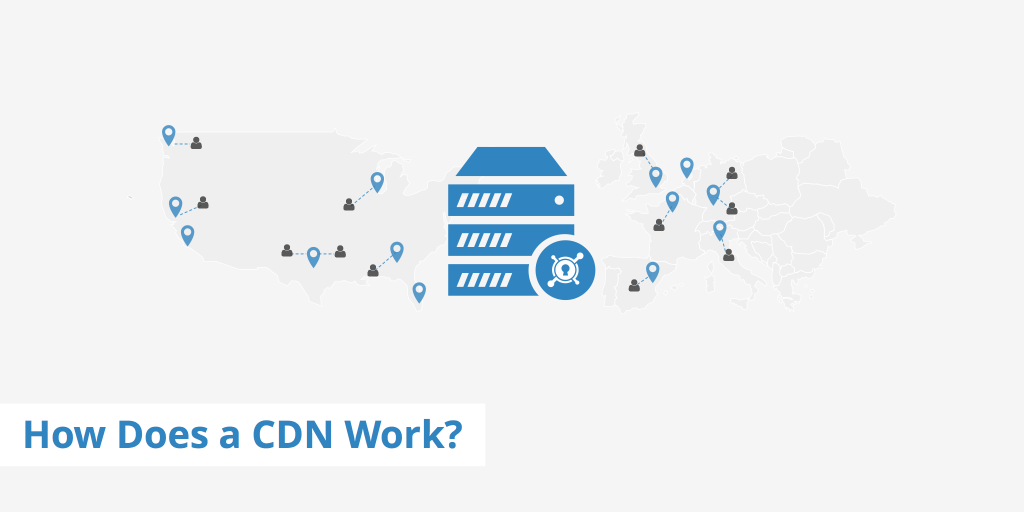
- Distributed Servers: CDNs have hosting servers (also called edge servers or points of presence, PoPs) located around the world. When a user requests content, directs them to the server geographically closest to them. This reduces the time it takes for the data to travel.
- Caching: CDNs store (or cache) copies of content, like HTML pages, images, and videos, on their servers. When a user requests content, instead of fetching it from the origin server (which could be far away), serves it from the nearest cached location.
- Load Balancing: Distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers to avoid overloading any single server, ensuring availability and optimal performance during high traffic periods.
- Redundancy & Reliability: In case one server fails or experiences issues, can automatically route the request to the next closest, operational server, ensuring high availability.
- Content Optimization: Some also optimize content by compressing files, minifying code, or using modern web standards (like HTTP/2) to further improve the delivery speed.
- Security: Many offer additional security features like DDoS protection, secure SSL certificates, and protection against malicious traffic, enhancing both the speed and safety of content delivery.
Benefits of Using a CDN:
- Improved Speed: Content is delivered faster since it comes from a server closer to the user.
- Reduced Latency: Lowering the distance between user and server helps minimize delay.
- Scalability: Handle large volumes of traffic and sudden spikes efficiently.
- Enhanced Security: With integrated security features, protect against cyberattacks.
- Global Reach: Make it easier to serve users around the globe with consistent performance.
Conclusion
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a crucial technology for enhancing the performance, speed, and reliability of delivering web content to users worldwide. By distributing content across a network of geographically dispersed servers, reduce latency, improve load times, and ensure that websites remain available and secure even during high traffic or cyberattacks. For any business or website aiming to provide a fast, scalable, and reliable user experience, implementing is a highly effective solution.





